
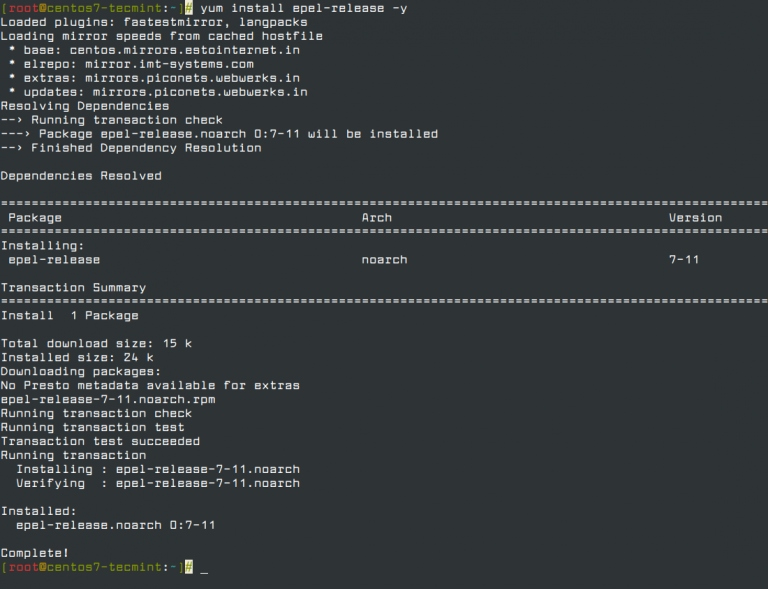
To upgrade the packages, use one of the following commands: yarn upgrade yarn upgrade yarn upgrade no package name is given, the command will update the project dependencies to their latest version according to the version range specified in the package.json file. You can open and edit this file at any time. Once completed, the script will create a basic package.json file that contains the information you provided. You can either answer or press enter to use the default values: yarn init v1.17.3 The script will ask you several questions. For example, to create a project named my_project you would type: yarn init my_project To create a new Yarn project use the yarn init command followed by the project name. Now that you have Yarn installed on your CentOS system, we’ll explore some of the most common Yarn commands. Verify the installation by printing the Yarn version number: yarn -versionĪt the time of writing this article, the latest version of Yarn is version 1.17.3. Once the repository is added, you can install Yarn, by running: sudo yum install yarn To enable the Yarn repository and import the repository’s GPG key issue the following commands: curl -silent -location | sudo tee /etc//yarn.repo sudo rpm -import The official Yarn repository is consistently maintained and provides the most up-to-date version. Install the Node.js package by typing: sudo yum install nodejs Installed on your system, enable the Nodesource repository with the following curl command
To install Yarn on your CentOS 7 system, follow the steps below: Prerequisites #īefore starting with the tutorial, make sure you are logged in as a user with sudo privileges On a CentOS 7 system from the Yarn RPM package repository. In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Yarn It was created to solve a set of problems with the npm such as speeding up the packages installation process by parallelizing operations and reducing errors related to network connectivity.
Install NodeJS on Ubuntu - Quick & Simple


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
